Five Trends in Regenerative Thermal Oxidizers Productivity
Published on: June 26, 2023 Topics: FLEXERAMIC ®, RTOA 21st birthday is cause for celebration—especially when it concerns the lifespan of capital equipment. The average lifespan of a regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO) can vary between ten to 20 years or even more. In fact, a well-designed RTO can outlast the personnel working at the facility. However, suppose you think a 20-year-old piece of capital equipment is outdated and not up to par with current operational demands, regulations or the newest efficiency equipment. In that case, the good news is that there are ways to update the RTO process to meet current trends.
The variability in efficiency, and lifespan, is directly linked to the condition and design of the ceramic heat exchange media. There is a choice of ceramic heat exchange media design, ranging from random packing to blocks with either a monolithic, straight-line design or a highly engineered, geometric structure. The efficiency of the RTO depends on this ceramic heat transfer media, and various trends in industrial processing highlight this dependency and the importance of proper selection.
Some of the current RTO trends or market factors include:
- RTO Energy Efficiency: A growing focus is on making RTOs more energy-efficient by reducing fuel consumption and optimizing their heat recovery capabilities. According to Oxford Economics, energy costs were listed as one of the three top challenges facing the manufacturing sector in 2022 and the near future. As a result, some new RTO designs use advanced materials and coatings to reduce heat loss and improve heat transfer efficiency, while others incorporate waste heat recovery systems to capture and reuse the heat generated by the oxidizer.
Geometrically structured packing material can increase the energy efficiency of an RTO, compared to monolithic ceramic packing media, by providing a larger surface area for heat transfer. The level of increased energy efficiency in an RTO with geometrically structured packing material compared to monolithic packing media will vary depending on the specific applications, operating conditions and particulate buildup. Geometrically structured packing also has the benefit of increased distribution once any type of plugging has occurred due to buildup.
- VOC Destruction Efficiency: Improving the destruction efficiency of RTOs is also an area of focus. This can be achieved through specialized catalysts, advanced combustion control systems, and real-time monitoring and optimization of the oxidizer operation.
Geometrically structured packing, such as FLEXERAMIC® structured packing, exclusive to Knight Material Technologies, can increase the destruction of VOCs in an RTO in several ways.
First, the geometrically arranged corrugated sheets offer increased surface area compared to random saddle or monolithic media. The increased surface area allows for more efficient and complete VOC oxidation.
The RTO structured packing media also creates a more turbulent mixing of the gas stream as it passes through the RTO. This enhances the mixing of the VOCs with the oxidizing agent, promoting more efficient oxidation and, therefore, greater VOC destruction efficiency.
As a third point, this design provides greater resistance to fouling over time, increasing gas flow efficiency by minimizing plugging common to monolithic media. This promotes the utilization of the entire heat transfer packing bed instead of a portion, which occurs once monolithic media becomes plugged.

FLEXERAMIC® structured packing is a geometric packing for RTOs - Flexibility: Many industries are looking for RTOs that are flexible and adaptable to changing process conditions and emissions profiles. This requires RTOs that can handle a wide range of flow rates, VOC concentrations and temperature variations.
The modular design of the structured heat transfer media, or the blocks, allows for customization and modification of RTO structured packing to meet specific process requirements. The geometrically structured packing media contributes to RTO flexibility by providing a higher turndown ratio. This enables the system to handle a wider range of flow rates and VOC concentrations while, at the same time, permitting the system to better withstand temperature variations. This is due to the robust construction and uniform distribution of packing material and the more uniform distribution of the gases within the tower.
The turndown ratio is between processes or equipment’s maximum and minimum capacity. In an RTO, this ratio refers to the range of flow rates and VOC concentrations the system can handle effectively while maintaining optimal performance.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: As with many other industrial processes, there is a trend towards remote monitoring and controlling RTOs using advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms. This enables operators to optimize the performance of the RTO in real time, reduce downtime, and improve overall efficiency.
Remote monitoring alerts operators of system malfunctions and allows for proactive maintenance and repairs. This can help prevent costly equipment failures and extend the lifespan of the RTO tower.
- Compliance with Emissions Regulations: Finally, increasingly stringent emissions regulations are key in developing new RTO packing material technologies. This includes the need for RTOs that can handle emissions from new types of industrial processes and operate at higher efficiencies and lower emissions levels than previous generations of RTOs.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets national ambient air quality standards (NAAQS) for harmful pollutants according to the Clean Air Act (CAA). It sets emissions standards for industries such as chemical plants, refineries and manufacturing facilities. The European Union regulates air quality under the Ambient Air Quality Directive, with regulations specific to industrial sources of air pollution. China and India also have standards to regulate air quality.
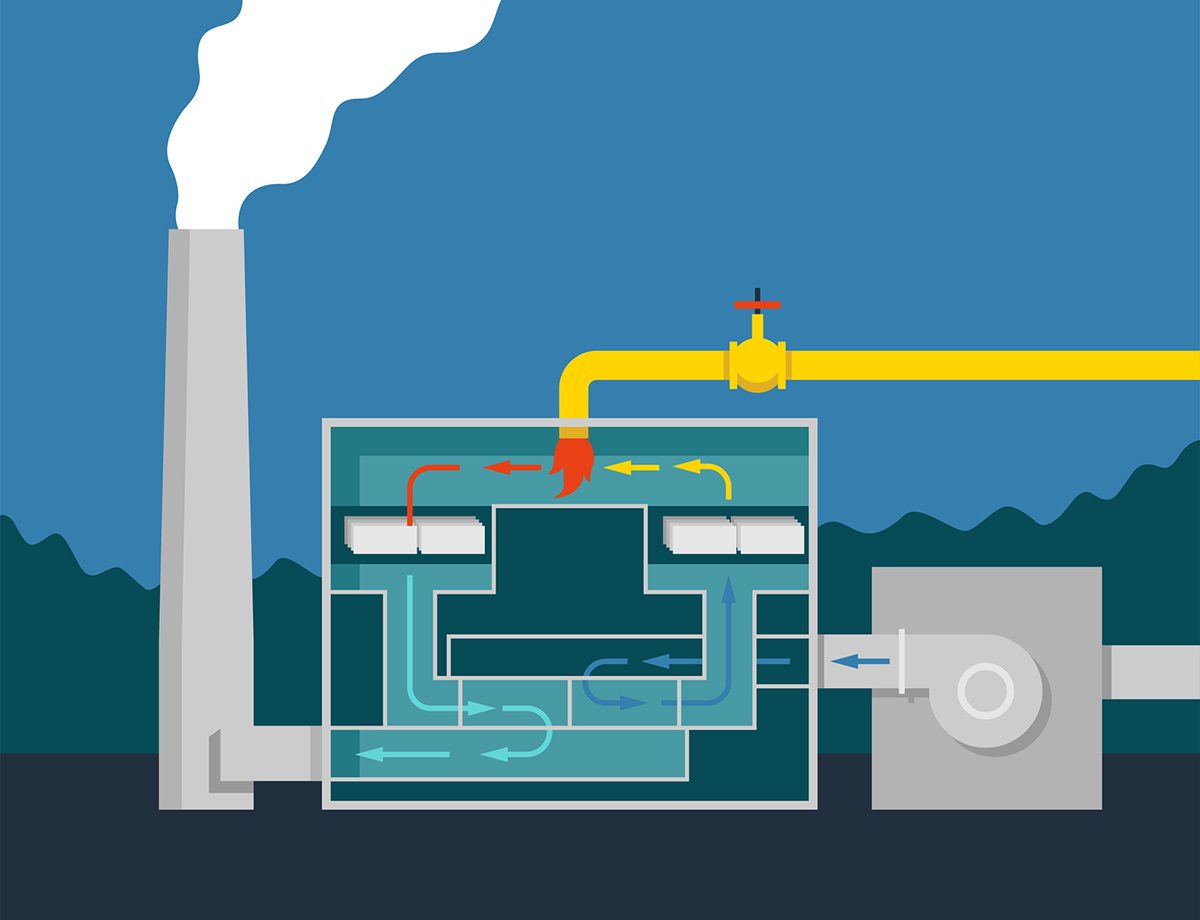
Increasing RTO efficiency is the first step in reducing energy costs
Realizing the impact of even a few select trends can help companies realize immense benefits. Complying with emissions regulations and using energy-efficient technologies like RTOs can help companies experience cost savings, avoid fines, extend the lifespan of capital equipment, and achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace. In addition, this RTO energy efficiency and compliance can help companies enhance brand reputation by demonstrating a commitment to environmental sustainability.
Want to talk about the latest in RTO packing material technology for a refurbishment or new installation? The engineering staff at Knight Material Technologies can support your next project from conception through completion. Meet and beat the trends with a call to Knight today.



